医脉通编译,转载请注明来源
2015年ASCO年会将于5月29日--6月2日在美国芝加哥召开,5月31日上午的非小细胞肺癌(NSCLC)口头报告专场,将公布rociletinib(CO-1686)治疗血浆基因型T790M阳性NSCLC患者的疗效。摘要结论表示,rociletinib治疗EGFR突变T790M阳性NSCLC患者可带来持续的缓解,且耐受性良好。
背景:Rociletinib是一种口服的EGFR突变抑制剂,包括T790M耐药突变。既往报告了500mg-1000mg BID(活性剂量)的rociletinib治疗肿瘤基因型T790M阳性患者的良好活性(NCT01526928)。该研究则报告通过血浆基因型检测的T790M阳性患者的数据。
方法:在总体的1/2期研究,患者为EGFR突变NSCLC患者,使用至少1个EGFR抑制剂治疗,ECOG PS 0-1。脑转移患者也被允许纳入。在2期研究中,要求通过中央肿瘤基因型确认为T790M阳性。通过BEAMing(Sysmex)评估血浆EGFR状态,使用微乳滴PCR之后流式细胞仪进行定量检测。
结果:345名患者被纳入接受活性剂量的治疗,平均年龄为62岁,66%女性,69%为ECOG 1,87%来自美国,平均既往治疗次数为3(45%≥2种TKI)。219名组织基因型患者和113名血浆基因型患者的缓解数据可获得。不管基因型检测方法是什么,T790M阳性患者的RECIST客观缓解率(ORR)约为48%。T790M阴性患者的ORR为33-36%(见下表)。
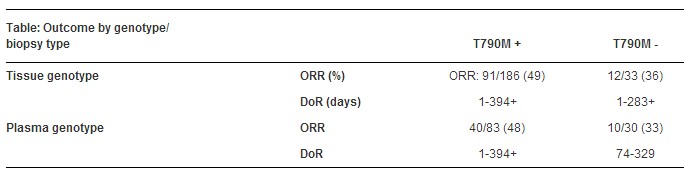
有17名患者血浆T790M阳性,但是组织基因型为阴性(9)或者失败(8),17人有5人缓解。16名患者组织T790M阳性,但是血浆组织分型阴性,6名患者缓解。8名患者两种方法检测均为阴性,有3名患者缓解。大多数T790M阴性的缓解者在接受rociletinib之前才刚刚接受过EGFR-TKI治疗(10/12组织和10/10血浆)。连续血浆数据显示出随着时间进展T790M水平的下降。
发生率≥15%的不良事件有:高血糖(40%),腹泻(28%),恶心(23%),乏力(21%),食欲下降(17%)。
结论:rociletinib治疗EGFR突变T790M阳性NSCLC患者可带来持续的缓解,且耐受性良好。三分之一的T790M患者也能缓解,这不能通过再治疗作用进行解释。连续血浆数据显示大多数患者的T790M下降,包括非缓解者,表明T790M并不总是主要的增长驱动因素。通过BEAMing进行的血浆基因分型在选择特定患者时可能是一种补充性的方法。临床试验信息:NCT01526928
会议专题》》》2015年ASCO年会专题报道
阅读摘要原文
Efficacy of rociletinib (CO-1686) in plasma-genotyped T790M-positive non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) patients (pts).(Abstract No:8001)
Author(s): Lecia V. Sequist, Jonathan Wade Goldman, Heather A. Wakelee, et al
Type: Oral Abstract Session
Background: Rociletinib is an oral inhibitor of mutant EGFR, including the T790M resistance mutation. We reported robust activity in T790M positive pts identified by tumor genotyping treated at 500mg-1000mg BID (active doses) [NCT01526928]. We now present data from the pt subset with T790M detected by plasma genotyping.
Methods: For the overall phase 1/2 study, pts had EGFR-mutant NSCLC and treatment with ≥ 1 EGFR inhibitor, ECOG PS 0-1. Brain metastases were allowed. In phase 2, T790M pos by central tumor genotyping was required. Plasma EGFR status was assessed by BEAMing (Sysmex), a quantitative assay using emulsion PCR then flow cytometry.
Results: 345 pts were enrolled at active doses, median age 62 yrs, 66% female, 69% ECOG 1, 87% from US sites, median prior therapies 3 (45% ≥ 2 prior TKIs). Response data are available for 219 with tissue genotyping and 113 with plasma genotyping. The RECIST objective response rate (ORR) was ~48% in T790M pos pts, regardless of genotyping method. ORR was 33-36% among T790M neg pts, (see Table). There were 17 pts T790M pos in plasma but with neg (9) or failed (8) tissue genotyping, and 5/17 responded. There were 16 pts T790M pos in tissue but with neg plasma genotyping and 6/16 responded. 3/8 who were neg by both methods responded. The majority of T790M negative responders were on an EGFR TKI immediately before rociletinib (10/12 tissue and 10/10 plasma). Serial plasma data typically showed a decrease in the levels of T790M over time. Related all grade AEs in ≥ 15% patients were: hyperglycemia (40%), diarrhea (28%), nausea (23%), fatigue (21%), decreased appetite (17%).
Conclusions: Rociletinib is associated with durable response and is well tolerated in pts with EGFR mutant T790Mpos NSCLC. One-third of T790M neg pts also respond, which cannot be explained by retreatment effect. Serial plasma data shows T790M decrease in most pts, including non-responders, suggesting T790M is not always the dominant growth driver. Plasma genotyping by BEAMing may be a complementary method to select patients. Clinical trial information: NCT01526928
