导语:近期的研究表明,对欧洲患者大规模的DNA及RNA测序揭示,肾癌的发生率与接触马兜铃酸有关。
国际癌症基因组肾癌联盟(CAGEKID)揭示了癌症与接触马兜铃酸(存在于草药中的一种成分)的重要关联。该研究由Scelo等于10月29日发表在Nature Communications上,这一发现对于公共健康有重要的意义。医脉通对该研究主要内容进行了报道。
研究全文:Scelo G,Nat Commun 2014 Oct 29
研究背景
每年约有140,000以上的人死于肾癌。在欧洲中部肾癌的发病率正在急剧增长。国际癌症基因组联盟的分支CAGEKID,在基因水平上研究了欧洲肾癌患者的致病因素。
研究方法
研究者对来自捷克,罗马尼亚,俄罗斯及英国的100位肾癌患者的正常细胞和肿瘤细胞进行了DNA及RNA测序。研究结果证实,这类癌症与某些特定基因的改变有关,并指出了特异的生物学途径及受突变影响的基因。
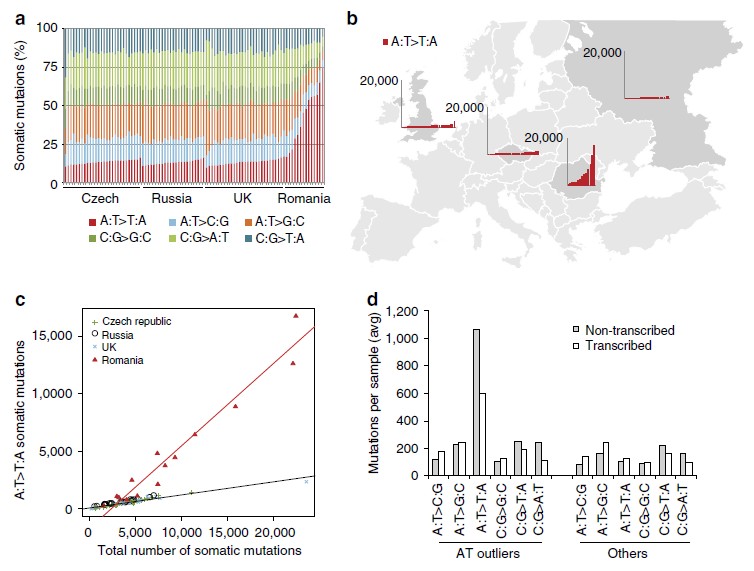
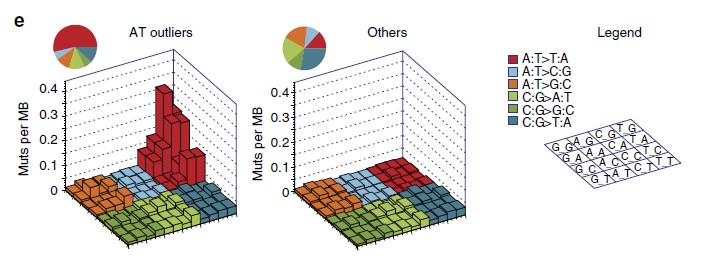
Figure 1 | Single-base substitution patterns in 94 ccRCC samples. (a) Proportion of observations within different base substitution classes for each ccRCC sample pair. (b) Number of A:T4T:A transversions in samples from the four countries included in the study. (c) The number of A:T4T:A transversions plotted against the total number of mutations in each sample. The graph also shows the linear regression lines for Romanian samples (red) and other samples (black). (d) Frequencies of six base substitution classes in Romanian outliers and other samples for somatic mutations within genes categorized into non-transcribed and transcribed strands. A:T4T:A transversions occur preferentially on the non-transcribed strand in the Romanian outliers. (e) Lego plot showing the number of somatic mutations with the surrounding sequence context for the Romanian outliers and other sample pairs. The plot illustrates the preference for A:T4T:A transversions within the context C/T[A:T]A/G, but also the overall increased frequency of A:T4T:A and increases of other mutational classes for the Romanian outliers.
研究结果
研究者发现在罗马尼亚的大部分患者中,高频率的基因变化与接触马兜铃酸有关,尽管对于这些患者如何接触到马兜铃酸尚不明确。但研究发现,肾癌的致病因素因人群的不同而异,证实了马兜铃酸是致癌物质。
该项研究由麦吉尔大学牵头,并完成了其中的DNA数据分析。该研究的通讯作者麦吉尔大学的Mark Lathrop教授表示, “研究共纳入了14名罗马尼亚患者,在12名患者中发现了特异性突变。在随后的研究中,我们将对来自罗马尼亚及巴尔干半岛其它地区的更多患者进行样本的分析。现在我们正在进行接触马兜铃酸程度的评估。“
研究带来的启示
国际癌症研究机构(IARC/WHO) 的 Ghislaine Scelo 强调,“这项肿瘤基因组研究的不同之处在于,研究的样本来自多个国家,致癌因素可能不同。我们的研究说明了通过大量基因测序对肿瘤DNA的系统性探索可以鉴别之前怀疑的致癌因素。”
医脉通编译自:New Research Shows Association of Kidney Cancer With Use of Aristolochic Acid,The Asco Post10/29/2014
